
Биохакинг
● Вишня, голубика, черника, черная смородина, слива и киви в маринадах эффективно снижают количество ГЦА[250].
● Добавление в маринад витамина Е снижает количество ГЦА[251].
● Добавление витамина С снижает количество гликотоксинов[252].
● Добавление куркумы снижает влияние гликотоксинов[253].
● Жарка в оливковом масле холодного отжима дает меньше всего ГЦА по сравнению с другими маслами, например рапсовым[254].
● Количество ППГ можно сократить, используя в маринаде кислые ингредиенты[255] (лимонный сок и уксус).
● Если во время жарки добавить глюкозу, это снизит количество потенциально канцерогенных веществ[256].
● Количество акриламида в картофеле можно снизить с помощью бланширования перед жаркой[257].
● Добавление перед выпеканием в тесто аминокислот (глицин и глутамин) снижает количество акриламида почти на 90 %[258].
Су-вид
По методу су-вид пища готовится под водой в вакуумном пакете и при тщательном контроле температурного режима.
Плюсы метода су-вид:
● Тщательный контроль за изменением ингредиентов под воздействием температуры.
● Температуру приготовления можно снизить.
● Время приготовления можно увеличить.
● Количество патогенов можно минимизировать посредством пастеризации.
● Предварительное доведение до полуготовности продлевает срок хранения, а также ускоряет и облегчает приготовление.
● Вкусовые качества, нутриенты и жидкости лучше сохраняются (особенно если речь об овощах – например, моркови)[259].
Минусы метода су-вид:
● Вакуумные пакеты для су-вида могут выделять токсины.
● Пакеты дороги и неэкологичны.
Для обеспечения безопасности следует обращать внимание на рекомендуемую температуру и время приготовления выбранного продукта. По опыту, готовка в течение часа и более при минимальной температуре 55 °C обычно позволяет уничтожить такие патогены, как листерия (Listeria), сальмонелла (Salmonella), хеликобактер пилори (Helicobacter pyroli) и трихинелла (Trichinella)[260].
СОВЕТПОПРОБУЙТЕ ПОЛОЖИТЬ В ПАКЕТ ДЛЯ СУ-ВИДА СЕМЕНА ГОРЧИЦЫ С БРОККОЛИ
Употребление с пищей свежей, термически не обработанной брокколи снижает мутагенное действие ГЦА[261] благодаря соединениям, богатым серой. Термическая обработка ослабляет активность этих соединений, но при использовании метода су-вид их свойства можно сохранить, добавив в пакет зерна горчицы[262].

РЕЦЕПТ
САМОДЕЛЬНЫЙ СУ-ВИДЕсли вы пока не готовы потратиться на устройство для су-вида, можете опробовать эту технологию дома с помощью подручных средств. Вам понадобятся только термометр, холодильный контейнер и водонепроницаемый пакет с застежкой. Поместите пищу в водонепроницаемый пакет. Опустите пакет в воду и выдавите остатки воздуха. Закройте пакет так, чтобы он был погружен в воду практически полностью. Наполните контейнер водой на 2 градуса теплее нужной температуры.
Поместите пакет в воду и закройте крышку. Проверяйте температуру воды каждые 20 минут. При необходимости добавляйте теплую воду для поддержания нужной температуры. Когда пройдет достаточно времени, достаньте пакет из воды. Приятного аппетита.
Пища, отваренная до полуготовности, быстро охлажденная и помещенная в холодильник в неоткрытом пакете для су-вида, хранится по крайней мере неделю (при замораживании – несколько месяцев). Добавление маринада или витаминов С или Е[263] в пакет для су-вида продлит срок хранения благодаря снижению окисления ингредиентов. Отдавайте предпочтение пакетам, не содержащим БФА, фталаты или пластификаторы. Обычно наиболее безопасны пакеты из полиэтилена или силикона.
Хранение
Человечество знает множество разных методов хранения пищи. В последние десятилетия пищевая промышленность добилась существенных успехов в разработке пищевых добавок и консервантов, а также внедрила новые методы промышленной обработки. Пища обычно хранится в холодильнике, морозилке или погребе. Кроме того, срок хранения различных продуктов можно увеличить, разумно подходя к выбору материалов для хранения, методов консервирования и полезных для здоровья высококачественных консервантов.
Откажитесь от пластиковых контейнеров для хранения пищи. Пользуйтесь керамической, металлической и стеклянной посудой.
Рекомендуемые подходы к хранению:
● защита от света в темных или тонированных контейнерах;
● защита от жары, например с помощью погреба или холодильника;
● защита от воздуха в герметичном контейнере или вакуумном пакете;
● сушка и сублимационная сушка;
● стерилизация при высокой температуре;
● предупреждение окисления при помощи сильных специй;
● предупреждение окисления с помощью витаминов C и E;
● упаковывание в модифицированной газовой среде (МГС), консервирование в меду, сахаре, алкоголе, уксусе, лимонном соке, соли или растительном масле.
Обеспечение достаточного потребления нутриентов
Рекомендации по потреблению нутриентов во многом основаны на массовых исследованиях дефицита питательных веществ и заболеваний, вызванных неполноценным питанием[264]. Однако эти рекомендации необязательно отражают оптимальный уровень нутриентов для конкретного человека – в силу генетических и эпигенетических факторов возможны значительные вариации. В любом организме постоянно происходят мутации. И эти мутации способны привести к уникальных различиям в последовательности ДНК[265].
С точки зрения диетологии эти отличия могут влиять на индивидуальные потребности в определенных микроэлементах и витаминах. Нередко мутации влияют напрямую на коферментную функцию витаминов и микроэлементов (например, цинка, витамина B6 или холина) и потребность организма в этих нутриентах[266]. Поэтому при составлении диетических рекомендаций оценка индивидуальных потребностей в нутриентах всегда должна быть первоочередной задачей.

Уровень нутриентов в значительной степени зависит от индивидуальной скорости усвоения. А при составлении общих диетических рекомендаций это учесть невозможно. Если пищеварение не справляется, нутриенты усваиваются хуже, чем ожидалось. Поэтому расчет оптимального уровня потребления нутриентов надо начинать с улучшения пищеварения.
Американский профессор биохимии и молекулярной биологии Брюс Эймс в течение нескольких десятилетий изучал рак и старение. Согласно его теории триажа микронутриентов и старения, организм использует запасы питательных веществ во внутренних органах, чтобы в условиях неполноценного питания поддерживать здоровье в краткосрочной перспективе. Например, в случае дефицита железа организм, чтобы нормально функционировать, обращается к запасам железа из печени. Но долгосрочный дефицит минералов и витаминов ослабляет организм и наносит ущерб ДНК и митохондриям[267]. Это может вызывать рак и ускорять старение. Для долголетия Эймс рекомендует удовлетворять потребности в микроэлементах на всех этапах жизни[268].
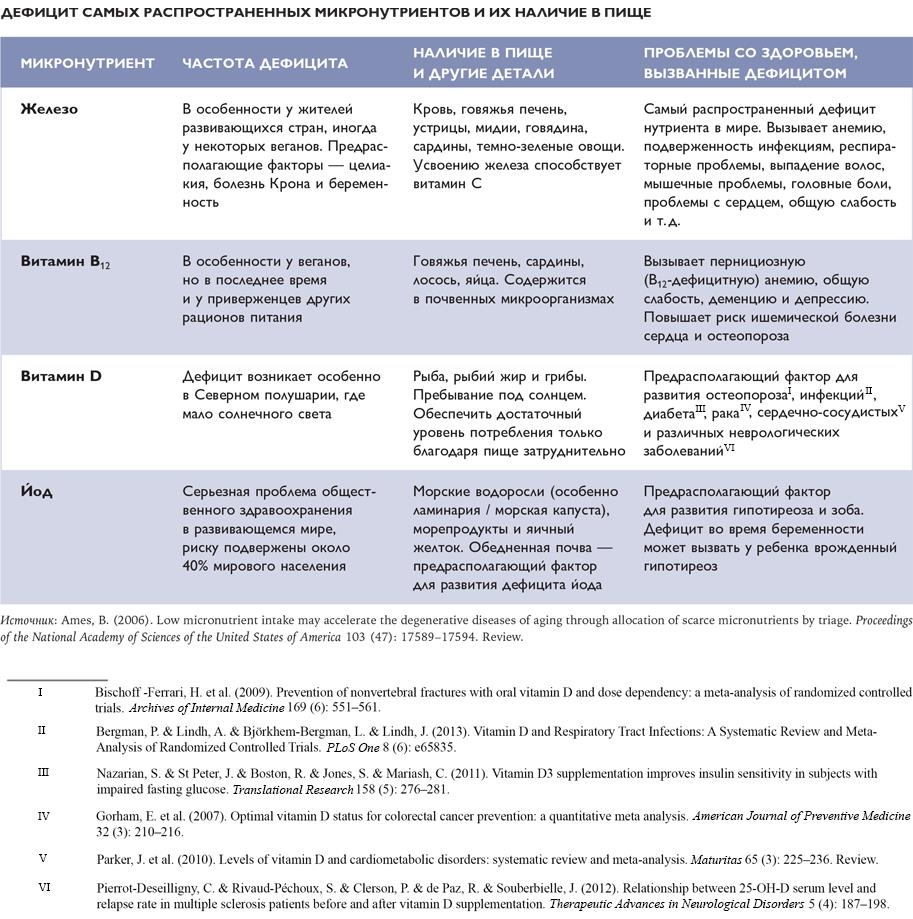
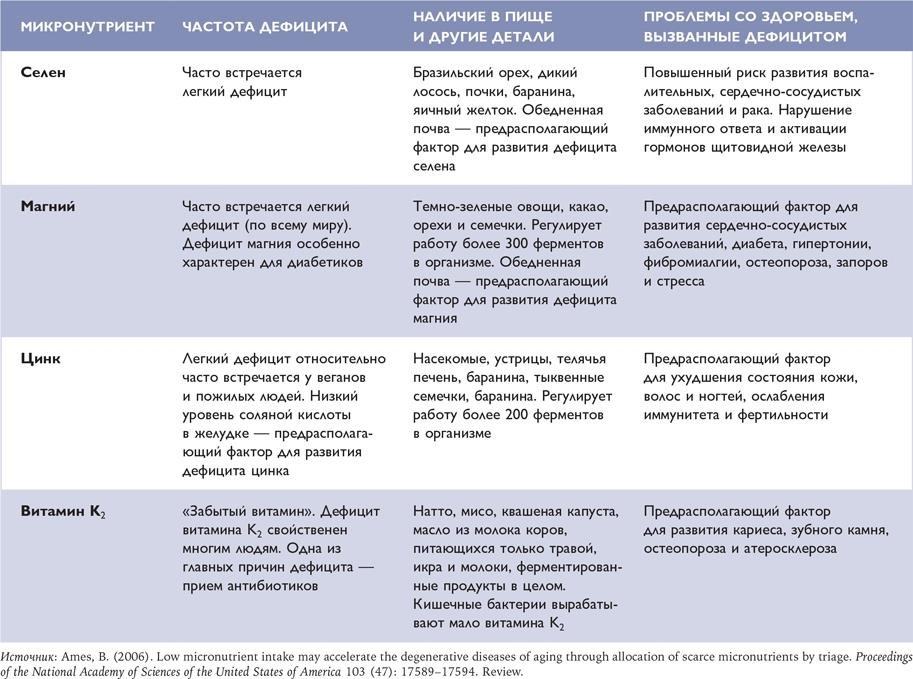
Оценка питания

Термин «калория» (от лат. calor – тепло) ввел в начале XIX в. французский химик и физик Николя Клеман-Дезорм (1779–1841)[269]. Калория – единица количества теплоты: энергия, необходимая для нагревания 1 г воды на один градус по Цельсию. Этот термин начал широко применяться в начале XX в. для измерения энергоемкости пищи[270]. Но в научной речи для обозначения единицы измерения энергии, выделяемой пищей, применяется официальный термин «килоджоуль».
Важность таких микроэлементов, как железо, йод и цинк, осознали еще в XIX в. Французский химик Жан-Батист Буссенго (1801–1887) доказал, что железо – жизненно важный нутриент для человека. Уже тогда было установлено, что дефицит железа вызывает зоб и врожденный гипотиреоз – заболевания, при которых щитовидная железа вырабатывает недостаточно тироксина. Во Франции школьникам давали йодные таблетки для профилактики зоба. В 1912 г. ученый из Кембриджского университета Фредерик Хопкинс (1861–1947) обнаружил, что для поддержания функций организма человеку в дополнение к макронутриентам нужны так называемые дополнительные пищевые факторы[271]. Позже эти пищевые факторы стали известны как витамины.
Концепция микронутриентов была введена в 30-х гг. прошлого века в контексте микроэлементов, необходимых растениям. Изучать рекомендуемые уровни потребления микронутриентов и их значение для здоровья начали в 1940-х гг. Согласно комплексным исследованиям, в промышленно развитых странах дефицит микронутриентов был очень частым явлением. Предложенное решение включало в себя введение в рацион рыбьего жира и модифицирование продуктов питания (например, добавление йода в соль)[272].

Биохакер измеряет функции своего организма, связанные с питанием, чтобы получить информацию о клетках крови, уровне витаминов, микро- и макронутриентов, микробиологическом статусе кишечника, особых генетических характеристиках и любых видах пищевой гиперчувствительности или аллергии.
ОЦЕНКА СТАТУСА ПИТАНИЯСамое разумное – понять, с чего вы начинаете, прежде чем вносить какие-либо существенные изменения в рацион или тратиться на пищевые добавки. Измерьте свои уровни нутриентов и ключевые показатели крови. Даже если вы чувствуете себя здоровыми, сдача анализов может быть полезна как профилактика.
● Уровни микронутриентов и микроэлементов:
– в крови;
– в волосах;
– в моче.
● Жирные кислоты:
– в крови.
● Аминокислоты:
– в крови;
– в моче.
● Тяжелые металлы:
– в крови;
– в волосах;
– в моче.
ОПРЕДЕЛЕНИЕ ПИЩЕВОЙ АЛЛЕРГИИ И ГИПЕРЧУВСТВИТЕЛЬНОСТИОчень важно выявить продукты питания, наносящие вред или ухудшающие функционирование организма. Их удаление из рациона существенно улучшает физическое и психологическое состояние, а главное – улучшает здоровье в целом.
Определение пищевой аллергии:
● пробная элиминационная диета (исключение «подозреваемого» продукта с параллельным ведением дневника симптомов. – Прим. науч. ред.);
● кожные пробы;
● анализы на антитела IgE и lgG;
● оральные провокационные пробы (молоко и злаки).
ИССЛЕДОВАНИЕ ФУНКЦИИ КИШЕЧНИКА И МИКРОБИОМАКачество работы кишечника и баланс микрофлоры могут очень быстро меняться. Эти изменения связаны с рядом заболеваний, которые можно предупредить или эффективно вылечить, проанализировав функциональность и микробиологический баланс кишечника. Физическое и психологическое состояние также тесно связаны с состоянием кишечника.
Исследование пищеварения:
● полный анализ пищеварения;
● оценка проницаемости кишечника и мальабсорбции;
● оценка возможного избыточного бактериального роста в тонкой кишке (ИБРТК);
● оценка кислотности желудочного сока и ферментов;
● анализ на Helicobacter pylori;
● антитела к глиадину (скрининг целиакии);
● уровень кальпротектина и панкреатической эластазы в кале.

Исследование микробиома:
● баланс микробиологического состава;
● штаммы полезных бактерий;
● штаммы вредоносных бактерий;
● дрожжевые грибы;
● амебы и другие паразиты.
ГЕНЕТИЧЕСКИЕ ТЕСТЫ И ПИТАНИЕДля выявления повышенного риска развития различных заболеваний (чтобы впоследствии учитывать этот риск при выборе образа жизни) широко применяются генетические тесты. Важно понимать, что образ жизни человека, включая питание, во многом определяет функционирование его генома. Не все гены постоянно активны. Эпигенетика – активация или дезактивация генов внешними для генома факторами – проявляется, например, в повышенной или пониженной функции определенных генов вследствие таких внешних факторов, как рацион питания.
Нутригеномика – наука, изучающая влияние питания на экспрессию генов. Например, норвежские ученые обнаружили, что сокращение потребления сахара (менее 40 % от энергоемкости принимаемой пищи) может снизить риск сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний, деменции, некоторых типов рака и диабета[273].
Подробнее о генетических тестах – в бонусных материалах онлайн:
biohack.to/nutrition
ДНЕВНИК ПИТАНИЯ
Отслеживайте следующие факторы питания:
● доля макронутриентов (углеводы, сахара, жиры);
● количество микронутриентов в потребляемой пище;
● уровень потребления калорий по сравнению с ежедневным расходом энергии (скорость основного обмена веществ и физическая активность);
● количество потребляемой воды (рекомендовано 1,5–2 л в день);
● количество потребляемого кофеина (рекомендовано максимум 400 мг в день);
● количество соли в потребляемой пище (рекомендовано максимум 5 г в день);
● регулярность приема пищи;
● фотографии потребляемых блюд;
● реакции на питание и изменения диеты.
Есть умные весы и приложения для смартфонов, которые определяют пищевую ценность продукта по штрихкоду на упаковке.
Обзор нутриентов


Менять рацион следует осторожно. Например, доказано, что популярные экстремальные диеты могут приводить к дефициту микронутриентов[274]. Но и обычная домашняя пища тоже не всегда отвечает диетическим рекомендациям.
В этой главе мы даем рекомендации по выбору более качественных, более богатых нутриентами индивидуальных ингредиентов. Несколько базовых принципов помогут легко исключить из рациона некачественные ингредиенты. Перефразируем Майкла Поллана, профессора Университета Беркли и директора стипендиальной программы Фонда Найтов «Научная и экологическая журналистика»: «Не покупайте ничего, что ваша бабушка полвека назад не приняла бы за еду». Это сразу исключает полуфабрикаты и готовую пищу, а также некачественные продукты.
Главное правило – чем ближе пища к естественному состоянию, тем вероятнее, что она обладает полезными для здоровья свойствами. Согласно метааналитическим исследованиям, в органических ингредиентах значительно больше антиоксидантов и меньше тяжелых металлов и пестицидов, чем в неорганических[275].
Соль
В странах Средиземноморья соль некогда ценилась не меньше золота. Солдатам римского легиона частично платили соляным пайком. Он назывался на латыни salarium argentum – «соляные деньги». Отсюда пошло и английское слово salary – «зарплата». Считается, что от латинского слова sal («соль») произошел и римский «салют»: он обозначает приветственный жест и связан с арабским «салям» – «мир».
Средний дневной уровень потребления соли в 2010 г. составлял около 10 г на человека. Примерно 80 % от этого количества – так называемая скрытая соль, содержащаяся в некоторых продуктах промышленного производства (например, из зерновых и мяса). К примеру, в хлебе соли может оказаться столько же, сколько в картофельных чипсах.
Рекомендуется снизить потребление поваренной соли, а также перейти на минеральную соль, богатую калием и магнием. Благодаря минеральной соли можно снизить артериальное давление, не снижая потребление соли в целом[276]. Важно помнить: хотя чрезмерное потребление соли и связывают с высоким артериальным давлением, недостаточное потребление соли – еще более серьезный риск для здоровья[277].

Высококачественная соль обогащает вкус пищи, является консервантом и поддерживает баланс жидкости в организме. Натрий жизненно необходим организму, чтобы передавать нервные импульсы, поддерживать работу мышц, а также регулировать баланс жидкости и артериальное давление. Хлор нужен для пищеварения и дыхания.
Природные соли либо получают путем выпаривания морской воды, либо добывают из донных морских и озерных отложений (такую соль перемалывают дома при помощи соляной мельницы). Учитывайте возможный риск загрязнения соли тяжелыми металлами (в том числе никелем) или микропластиком (от дешевых соляных мельниц). Качество соли также зависит от чистоты моря и зоны, где обрабатывают соль.
Кое-где йодируют поваренную соль, чтобы решить проблему йододефицита. Однако соль – далеко не лучший источник йода. Например, 1 ч. л. морской капусты содержит столько же йода, сколько 0,5 кг йодированной морской соли.
СОВЕТСМЕШИВАЙТЕ РАЗНЫЕ ВИДЫ СОЛИ
Например, морскую, розовую и черную соль. Добавляйте сухие приправы по вкусу (розмарин, базилик, мяту). Это повышает плотность нутриентов и придает соли аромат.

● экологически чистую нерафинированную морскую соль;
● розовую соль под различными названиями (гималайская соль, каменная соль, галит);
● черную соль;
● морскую соль с травами;
● редкие специальные соли (бамбуковую, речную).

● обычную рафинированную и поваренную соль;
● пряную соль (с глутаматом натрия, МНГ).
Сахар
Средний житель США потребляет свыше 126 г сахара в день. Это более чем вдвое выше дневной нормы, рекомендованной Всемирной организацией здравоохранения. Около 70–80 % этого сахара – так называемый скрытый сахар. Он в избытке содержится в продуктах промышленного производства (йогурт, сок, сладкая газировка, мясная нарезка, пицца, соевый соус, майонез), полуфабрикатах и готовой пище.
В отличие от тростникового сахара, белый рафинированный сахар не содержит микроэлементов или минералов. Он может мешать усвоению кальция, магния, цинка и железа, а также расходует запасы микроэлементов и минералов в организме – они требуются для метаболизма сахара.
С чрезмерным употреблением белого сахара связывают нарушения обмена веществ – например, диабет 2-го типа и метаболический синдром[278], нарушение метаболизма жиров и системное воспаление, сердечно-сосудистые заболевания[279],[280],[281] и болезнь Альцгеймера[282],[283]. Кроме того, сахар и фруктоза перегружают печень[284]. А самое неприятное – сахар, согласно исследованиям, вызывает физическую зависимость[285].
Лучше заменить белый сахар на альтернативы, содержащие микроэлементы, а также избегать источников скрытого сахара (йогурт с добавками, сок, сладкая газировка, полуфабрикаты).

● непастеризованный и нефильтрованный мед;
● местный мед, не подвергавшийся обработке, произведенный в экологически чистом районе и собранный на одной пасеке;
● мед разных сортов (например, гречишный, липовый, каштановый);
● чем темнее цвет меда, тем лучше.
Мед дает хорошие результаты в лечении острого кашля у детей[286],[287], а также в составе десенсибилизационной терапии при аллергических заболеваниях.

РЕЦЕПТ
МЕД С ТРАВАМИ[288]Смешайте с медом натуральную ваниль, спирулину или семена крапивы. Мед – отличный консервант, а смешанные с ним пряности или травы придают ему приятный привкус.

● кокосовый сахар;
● цельный тростниковый сахар (нерафинированный и минимально обработанный, часто продается под непривычными названиями: индийский (гур), рападура или кокуто).

● белый сахар;
● коричневый сахар (частично отбеленный сырой тростниковый сахар, также продается под непривычными названиями: демерара или мелассовый сахар);
● сахар для выпечки (в том числе сахар для глазури, мягкий коричневый сахар, ванильный сахар);
● фруктозу.
ПОДСЛАСТИТЕЛИ ВЫСОКОЙ ИНТЕНСИВНОСТИ[289] И САХАРНЫЕ СПИРТЫ
● ксилит;
● зеленую стевию (листья растения).

● генетически модифицированный ксилит;
● эритрит;
● сорбит;
● экстракт стевиол-гликозида (белая стевия);
● аспартам;
● ацесульфам K.

● кленовый сироп;
● кокосовый сироп;
● сироп из якона;
● еловый сироп;
● пальмовый сироп (китульской пальмы Caryotaurens).

● глюкозно-фруктозный сироп (кукурузный сахар);
● сироп агавы, сахарный сироп, купажный сироп.
ДРУГОЕПри необходимости употребляйте в качестве подсластителя:
● луо хан гуо (архат);
● лукуму;
● кактус нопаль (опунция);
● инулин;
● корень солодки (лакрица).
Специи
Специи используются для улучшения вкуса и для консервирования. Это могут быть части пряно-ароматических растений, а также растительные компоненты или минералы.
Многие специи обладают как целебными, укрепляющими здоровье, так и профилактическими свойствами. Некоторые специи также стимулируют работу пищеварительной системы.
Вкус и аромат специям придает окисление и испарение растительного сырья. Поэтому молотые специи постепенно теряют вкус и лечебные свойства. Цельные специи хранятся около двух лет, а молотые – примерно шесть месяцев, однако их вкус может ухудшиться гораздо раньше.

● дикорастущие пряности;
● свежие имбирь и куркуму;
● чеснок и луковые;
● перец чили, кайенский и черный;
● цейлонскую корицу, кардамон, тмин, фенхель и лавровый лист;
● розмарин, орегано, тимьян, укроп, эстрагон, кориандр, мяту, базилик, петрушку и шалфей;
● травы из собственного мини-огородика у окна или на балконе;
● органические специи в цельном виде (не молотые).

● специи, дезинфицированные радиацией (ионизирующим излучением);
● мельнички с просроченными специями, которые находились под постоянным воздействием света, тепла и влаги;
● специи, долго хранившиеся над варочной панелью (могут быть заражены плесенью).

Кумарин – природное ароматическое соединение, содержащееся во многих растениях. Главный его источник в пище – корица. Коричник китайский (Cinnamomum cassia), чаще всего использующийся в Европе и США, содержит кумарин в больших количествах. В более редкой и дорогой цейлонской корице кумарина очень мало. Кумарин токсичен для печени (гепатотоксичен) – правда, для токсичной концентрации нужно регулярно употреблять более 2 ч. л. корицы в день. В 2004 г. Европейское агентство по безопасности продуктов питания (ЕАБПП) установило предельно допустимую дневную норму кумарина – 0,1 мг на 1 кг веса. Регулярное неограниченное употребление корицы не рекомендуется.