
The Stones of Venice, Volume 2 (of 3)
§ XV. First, for its proportions: I shall have occasion in Chapter V. to dwell at some length on the peculiar subtlety of the early Venetian perception for ratios of magnitude; the relations of the sides of this heptagonal apse supply one of the first and most curious instances of it. The proportions above given of the nave and aisles might have been dictated by a mere love of mathematical precision; but those of the apse could only have resulted from a true love of harmony.
In fig. 6, Plate I. the plan of this part of the church is given on a large scale, showing that its seven external sides are arranged on a line less than a semicircle, so that if the figure were completed, it would have sixteen sides; and it will be observed also, that the seven sides are arranged in four magnitudes, the widest being the central one. The brickwork is so much worn away, that the measures of the arches are not easily ascertainable, but those of the plinth on which they stand, which is nearly uninjured, may be obtained accurately. This plinth is indicated by the open line in the ground plan, and its sides measure respectively:

§ XVI. Now observe what subtle feeling is indicated by this delicacy of proportion. How fine must the perceptions of grace have been in those builders who could not be content without some change between the second and third, the fifth and sixth terms of proportion, such as should oppose the general direction of its cadence, and yet were content with a diminution of two inches on a breadth of seven feet and a half! For I do not suppose that the reader will think the curious lessening of the third and fifth arch a matter of accident, and even if he did so, I shall be able to prove to him hereafter that it was not, but that the early builders were always desirous of obtaining some alternate proportion of this kind. The relations of the numbers are not easily comprehended in the form of feet and inches, but if we reduce the first four of them into inches, and then subtract some constant number, suppose 75, from them all, the remainders 4, 16, 14, 19, will exhibit the ratio of proportion in a clearer, though exaggerated form.
§ XVII. The pairs of circular spots at b, c, d, etc., on the ground plan fig. 6, represent the bearing shafts, which are all of solid marble as well as their capitals. Their measures and various other particulars respecting them are given in Appendix 6. “Apse of Murano;” here I only wish the reader to note the coloring of their capitals. Those of the two single shafts in the angles (a, h) are both of deep purple marble; the two next pairs, b and g, are of white marble; the pairs c and f are of purple, and d and e are of white: thus alternating with each other on each side; two white meeting in the centre. Now observe, the purple capitals are all left plain; the white are all sculptured. For the old builders knew that by carving the purple capitals they would have injured them in two ways: first, they would have mixed a certain quantity of grey shadow with the surface hue, and so adulterated the purity of the color; secondly, they would have drawn away the thoughts from the color, and prevented the mind from fixing upon it or enjoying it, by the degree of attention which the sculpture would have required. So they left their purple capitals full broad masses of color; and sculptured the white ones, which would otherwise have been devoid of interest.
§ XVIII. But the feature which is most to be noted in this apse is a band of ornament, which runs round it like a silver girdle, composed of sharp wedges of marble, preciously inlaid, and set like jewels into the brickwork; above it there is another band of triangular recesses in the bricks, of nearly similar shape, and it seems equally strange that all the marbles should have fallen from it, or that it should have been originally destitute of them. The reader may choose his hypothesis; but there is quite enough left to interest us in the lower band, which is fortunately left in its original state, as is sufficiently proved by the curious niceties in the arrangement of its colors, which are assuredly to be attributed to the care of the first builder. A word or two, in the first place, respecting the means of color at his disposal.
§ XIX. I stated that the building was, for the most part, composed of yellow brick. This yellow is very nearly pure, much more positive and somewhat darker than that of our English light brick, and the material of the brick is very good and hard, looking, in places, almost vitrified, and so compact as to resemble stone. Together with this brick occurs another of a deep full red, and more porous substance, which is used for decoration chiefly, while all the parts requiring strength are composed of the yellow brick. Both these materials are cast into any shape and size the builder required, either into curved pieces for the arches, or flat tiles for filling the triangles; and, what is still more curious, the thickness of the yellow bricks used for the walls varies considerably, from two inches to four; and their length also, some of the larger pieces used in important positions being a foot and a half long.
With these two kinds of brick, the builder employed five or six kinds of marble: pure white, and white veined with purple; a brecciated marble of white and black; a brecciated marble of white and deep green; another, deep red, or nearly of the color of Egyptian porphyry; and a grey and black marble, in fine layers.
§ XX. The method of employing these materials will be understood at once by a reference to the opposite plate (Plate III.), which represents two portions of the lower band. I could not succeed in expressing the variation and chequering of color in marble, by real tints in the print; and have been content, therefore, to give them in line engraving. The different triangles are, altogether, of ten kinds:
a. Pure white marble with sculptured surface (as the third and fifth in the upper series of Plate III.).
b. Cast triangle of red brick with a sculptured round-headed piece of white marble inlaid (as the first and seventh of the upper series, Plate III.).
c. A plain triangle of greenish black marble, now perhaps considerably paler in color than when first employed (as the second and sixth of the upper series of Plate III.).
d. Cast red brick triangle, with a diamond inlaid of the above-mentioned black marble (as the fourth in the upper series of Plate III.).
e. Cast white brick, with an inlaid round-headed piece of marble, variegated with black and yellow, or white and violet (not seen in the plate).
f. Occurs only once, a green-veined marble, forming the upper part of the triangle, with a white piece below.
g. Occurs only once. A brecciated marble of intense black and pure white, the centre of the lower range in Plate III.
h. Sculptured white marble with a triangle of veined purple marble inserted (as the first, third, fifth, and seventh of the lower range in Plate III.).
i. Yellow or white marble veined with purple (as the second and sixth of the lower range in Plate III.).
k. Pure purple marble, not seen in this plate.
III.

Inlaid Bands of Murano.
§ XXI. The band, then, composed of these triangles, set close to each other in varied but not irregular relations, is thrown, like a necklace of precious stones, round the apse and along the ends of the aisles; each side of the apse taking, of course, as many triangles as its width permits. If the reader will look back to the measures of the sides of the apse, given before, p. 42, he will see that the first and seventh of the series, being much narrower than the rest, cannot take so many triangles in their band. Accordingly, they have only six each, while the other five sides have seven. Of these groups of seven triangles each, that used for the third and fifth sides of the apse is the uppermost in Plate III.; and that used for the centre of the apse, and of the whole series, is the lowermost in the same plate; the piece of black and white marble being used to emphasize the centre of the chain, exactly as a painter would use a dark touch for a similar purpose.
§ XXII. And now, with a little trouble, we can set before the reader, at a glance, the arrangement of the groups along the entire extremity of the church.
There are thirteen recesses, indicative of thirteen arches, seen in the ground plan, fig. 2, Plate I. Of these, the second and twelfth arches rise higher than the rest; so high as to break the decorated band; and the groups of triangles we have to enumerate are, therefore, only eleven in number; one above each of the eleven low arches. And of these eleven, the first and second, tenth and eleventh, are at the ends of the aisles; while the third to the ninth, inclusive, go round the apse. Thus, in the following table, the numerals indicate the place of each entire group (counting from the south to the north side of the church, or from left to right), and the letters indicate the species of triangle of which it is composed, as described in the list given above.

The central group is put first, that it may be seen how the series on the two sides of the apse answer each other. It was a very curious freak to insert the triangle e, in the outermost place but one of both the fourth and eighth sides of the apse, and in the outermost but two in the third and ninth; in neither case having any balance to it in its own group, and the real balance being only effected on the other side of the apse, which it is impossible that any one should see at the same time. This is one of the curious pieces of system which so often occur in mediæval work, of which the key is now lost. The groups at the ends of the transepts correspond neither in number nor arrangement; we shall presently see why, but must first examine more closely the treatment of the triangles themselves, and the nature of the floral sculpture employed upon them.
IV.

SCULPTURES OF MURANO.
§ XXIII. As the scale of Plate III. is necessarily small, I have given three of the sculptured triangles on a larger scale in Plate IV. opposite. Fig. 3 is one of the four in the lower series of Plate IV., and figs. 4 and 5 from another group. The forms of the trefoils are here seen more clearly; they, and all the other portions of the design, are thrown out in low and flat relief, the intermediate spaces being cut out to the depth of about a quarter of an inch. I believe these vacant spaces were originally filled with a black composition, which is used in similar sculptures at St. Mark’s, and of which I found some remains in an archivolt moulding here, though not in the triangles. The surface of the whole would then be perfectly smooth, and the ornamental form relieved by a ground of dark grey; but, even though this ground is lost, the simplicity of the method insures the visibility of all its parts at the necessary distance (17 or 18 feet), and the quaint trefoils have a crispness and freshness of effect which I found it almost impossible to render in a drawing. Nor let us fail to note in passing how strangely delightful to the human mind the trefoil always is. We have it here repeated five or six hundred times in the space of a few yards, and yet are never weary of it. In fact, there are two mystical feelings at the root of our enjoyment of this decoration: the one is the love of trinity in unity, the other that of the sense of fulness with order; of every place being instantly filled, and yet filled with propriety and ease; the leaves do not push each other, nor put themselves out of their own way, and yet whenever there is a vacant space, a leaf is always ready to step in and occupy it.
§ XXIV. I said the trefoil was five or six hundred times repeated. It is so, but observe, it is hardly ever twice of the same size; and this law is studiously and resolutely observed. In the carvings a and b of the upper series, Plate III., the diminution of the leaves might indeed seem merely representative of the growth of the plant. But look at the lower: the triangles of inlaid purple marble are made much more nearly equilateral than those of white marble, into whose centres they are set, so that the leaves may continually diminish in size as the ornament descends at the sides. The reader may perhaps doubt the accuracy of the drawing on the smaller scale, but in that given larger, fig. 3, Plate IV., the angles are all measured, and the purposeful variation of width in the border therefore admits of no dispute.14 Remember how absolutely this principle is that of nature; the same leaf continually repeated, but never twice of the same size. Look at the clover under your feet, and then you will see what this Murano builder meant, and that he was not altogether a barbarian.
§ XXV. Another point I wish the reader to observe is, the importance attached to color in the mind of the designer. Note especially—for it is of the highest importance to see how the great principles of art are carried out through the whole building—that, as only the white capitals are sculptured below, only the white triangles are sculptured above. No colored triangle is touched with sculpture; note also, that in the two principal groups of the apse, given in Plate III., the centre of the group is color, not sculpture, and the eye is evidently intended to be drawn as much to the chequers of the stone, as to the intricacies of the chiselling. It will be noticed also how much more precious the lower series, which is central in the apse, is rendered, than the one above it in the plate, which flanks it: there is no brick in the lower one, and three kinds of variegated marble are used in it, whereas the upper is composed of brick, with black and white marble only; and lastly—for this is especially delightful—see how the workman made his chiselling finer where it was to go with the variegated marbles, and used a bolder pattern with the coarser brick and dark stone. The subtlety and perfection of artistical feeling in all this are so redundant, that in the building itself the eye can rest upon this colored chain with the same kind of delight that it has in a piece of the embroidery of Paul Veronese.
Fig. II.
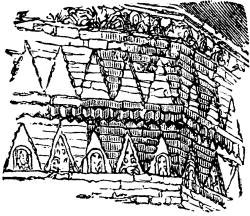
§ XXVI. Such being the construction of the lower band, that of the upper is remarkable only for the curious change in its proportions. The two are separated, as seen in the little woodcut here at the side, by a string-course composed of two layers of red bricks, of which the uppermost projects as a cornice, and is sustained by an intermediate course of irregular brackets, obtained by setting the thick yellow bricks edgeways, in the manner common to this day. But the wall above is carried up perpendicularly from this projection, so that the whole upper band is advanced to the thickness of a brick over the lower one. The result of this is, of course, that each side of the apse is four or five inches broader above than below; so that the same number of triangles which filled a whole side of the lower band, leave an inch or two blank at each angle in the upper. This would have looked awkward, if there had been the least appearance of its being an accidental error; so that, in order to draw the eye to it, and show that it is done on purpose, the upper triangles are made about two inches higher than the lower ones, so as to be much more acute in proportion and effect, and actually to look considerably narrower, though of the same width at the base. By this means they are made lighter in effect, and subordinated to the richly decorated series of the lower band, and the two courses, instead of repeating, unite with each other, and become a harmonious whole.
V.

Archivolt in the Duomo of Murano.
In order, however, to make still more sure that this difference in the height of the triangles should not escape the eye, another course of plain bricks is added above their points, increasing the width of the band by another two inches. There are five courses of bricks in the lower band, and it measures 1 ft. 6 in. in height: there are seven courses in the upper (of which six fall between the triangles), and it measures 1 ft. 10 in. in height, except at the extremity of the northern aisle, where for some mysterious reason the intermediate cornice is sloped upwards so as to reduce the upper triangles to the same height as those below. And here, finally, observe how determined the builder was that the one series should not be a mere imitation of the other; he could not now make them acute by additional height—so he here, and here only, narrowed their bases, and we have seven of them above, to six below.
§ XXVII. We come now to the most interesting portion of the whole east end, the archivolt at the end of the northern aisle.
It was above stated, that the band of triangles was broken by two higher arches at the ends of the aisles. That, however, on the northern side of the apse does not entirely interrupt, but lifts it, and thus forms a beautiful and curious archivolt, drawn opposite, in Plate V. The upper band of triangles cannot rise together with the lower, as it would otherwise break the cornice prepared to receive the second story; and the curious zigzag with which its triangles die away against the sides of the arch, exactly as waves break upon the sand, is one of the most curious features in the structure.
It will be also seen that there is a new feature in the treatment of the band itself when it turns the arch. Instead of leaving the bricks projecting between the sculptured or colored stones, reversed triangles of marble are used, inlaid to an equal depth with the others in the brickwork, but projecting beyond them so as to produce a sharp dark line of zigzag at their junctions. Three of these supplementary stones have unhappily fallen out, so that it is now impossible to determine the full harmony of color in which they were originally arranged. The central one, corresponding to the keystone in a common arch, is, however, most fortunately left, with two lateral ones on the right hand, and one on the left.
§ XXVIII. The keystone, if it may be so called, is of white marble, the lateral voussoirs of purple; and these are the only colored stones in the whole building which are sculptured; but they are sculptured in a way which, more satisfactorily proves that the principle above stated was understood by the builders, than if they had been left blank. The object, observe, was to make the archivolt as rich as possible; eight of the white sculptured marbles were used upon it in juxtaposition. Had the purple marbles been left altogether plain, they would have been out of harmony with the elaboration of the rest. It became necessary to touch them with sculpture as a mere sign of carefulness and finish, but at the same time destroying their colored surface as little as possible. The ornament is merely outlined upon them with a fine incision, as if it had been etched out on their surface preparatory to being carved. In two of them it is composed merely of three concentric lines, parallel with the sides of the triangle; in the third, it is a wreath of beautiful design, which I have drawn of larger size in fig. 2, Plate V., that the reader may see how completely the surface is left undestroyed by the delicate incisions of the chisel, and may compare the method of working with that employed on the white stones, two of which are given in that plate, figs. 4 and 5. The keystone, of which we have not yet spoken, is the only white stone worked with the light incision; its design not being capable of the kind of workmanship given to the floral ornaments, and requiring either to be carved in complete relief, or left as we see it. It is given at fig. 1 of Plate IV. The sun and moon on each side of the cross are, as we shall see in the fifth Chapter, constantly employed on the keystones of Byzantine arches.
§ XXIX. We must not pass without notice the grey and green pieces of marble inserted at the flanks of the arch. For, observe, there was a difficulty in getting the forms of the triangle into anything like reconciliation at this point, and a mediæval artist always delights in a difficulty: instead of concealing it, he boasts of it; and just as we saw above that he directed the eye to the difficulty of filling the expanded sides of the upper band by elongating his triangles, so here, having to put in a piece of stone of awkward shape, he makes that very stone the most conspicuous in the whole arch, on both sides, by using in one case a dark, cold grey; in the other a vigorous green, opposed to the warm red and purple and white of the stones above and beside it. The green and white piece on the right is of a marble, as far as I know, exceedingly rare. I at first thought the white fragments were inlaid, so sharply are they defined upon their ground. They are indeed inlaid, but I believe it is by nature; and that the stone is a calcareous breccia of great mineralogical interest. The white spots are of singular value in giving piquancy to the whole range of more delicate transitional hues above. The effect of the whole is, however, generally injured by the loss of the three large triangles above. I have no doubt they were purple, like those which remain, and that the whole arch was thus one zone of white, relieved on a purple ground, encircled by the scarlet cornices of brick, and the whole chord of color contrasted by the two precious fragments of grey and green at either side.
§ XXX. The two pieces of carved stone inserted at each side of the arch, as seen at the bottom of Plate V., are of different workmanship from the rest; they do not match each other, and form part of the evidence which proves that portions of the church had been brought from the mainland. One bears an inscription, which, as its antiquity is confirmed by the shapelessness of its letters, I was much gratified by not being able to read; but M. Lazari, the intelligent author of the latest and best Venetian guide, with better skill, has given as much of it as remains, thus:

I have printed the letters as they are placed in the inscription, in order that the reader may form some idea of the difficulty of reading such legends when the letters, thus thrown into one heap, are themselves of strange forms, and half worn away; any gaps which at all occur between them coming in the wrong places. There is no doubt, however, as to the reading of this fragment:—“T … Sancte Marie Domini Genetricis et beati Estefani martiri ego indignus et peccator Domenicus T.” On these two initial and final T’s, expanding one into Templum, the other into Torcellanus, M. Lazari founds an ingenious conjecture that the inscription records the elevation of the church under a certain bishop Dominic of Torcello (named in the Altinat Chronicle), who flourished in the middle of the ninth century. If this were so, as the inscription occurs broken off on a fragment inserted scornfully in the present edifice, this edifice must be of the twelfth century, worked with fragments taken from the ruins of that built in the ninth. The two T’s are, however, hardly a foundation large enough to build the church upon, a hundred years before the date assigned to it both by history and tradition (see above, § VIII.): and the reader has yet to be made aware of the principal fact bearing on the question.
§ XXXI. Above the first story of the apse runs, as he knows already, a gallery under open arches, protected by a light balustrade. This balustrade is worked on the outside with mouldings, of which I shall only say at present that they are of exactly the same school as the greater part of the work of the existing church. But the great horizontal pieces of stone which form the top of this balustrade are fragments of an older building turned inside out. They are covered with sculptures on the back, only to be seen by mounting into the gallery. They have once had an arcade of low wide arches traced on their surface, the spandrils filled with leafage, and archivolts enriched with studded chainwork and with crosses in their centres. These pieces have been used as waste marble by the architect of the existing apse. The small arches of the present balustrade are cut mercilessly through the old work, and the profile of the balustrade is cut out of what was once the back of the stone; only some respect is shown for the crosses in the old design, the blocks are cut so that these shall be not only left uninjured, but come in the centre of the balustrades.